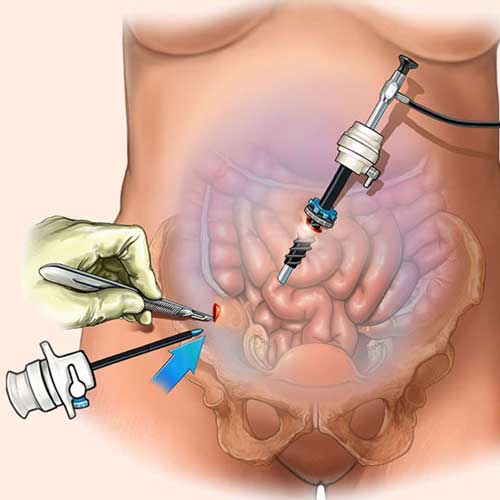
Our Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Centre specializes in minimally invasive procedures, ensuring faster recovery, reduced pain, and minimal scarring. With state-of-the-art technology and expert surgeons, we provide precise and effective treatment for various conditions.
- Appendix Surgery (Laparoscopic Appendectomy) – Quick and precise removal of an inflamed appendix.
- Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery – Weight loss surgeries, including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass.
- Hernia Repair (Laparoscopic Hernioplasty) – Minimally invasive treatment for inguinal, umbilical, and incisional hernias.
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy – Advanced uterine surgery with minimal discomfort and quicker recovery.
- Laparoscopic Fundoplication – Surgical treatment for GERD (acid reflux disease).
- Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery – Minimally invasive treatment for colorectal cancer and other bowel disorders.
Precision, expertise, and faster recovery with minimally invasive surgery.
Appendix Surgery (Laparoscopic Appendectomy)
Quick and precise removal of an inflamed appendix
Introduction to Appendix Surgery
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a modern, minimally invasive procedure used to remove an inflamed or infected appendix, a condition known as appendicitis. This surgical approach has largely replaced traditional open surgery due to its precision, reduced pain, and quicker recovery. Appendicitis is considered a medical emergency, and prompt surgical removal of the appendix prevents complications such as rupture or infection.
How the Procedure Works
During a laparoscopic appendectomy, surgeons make small incisions in the abdomen and insert a camera and specialized instruments. The inflamed appendix is carefully detached and removed through one of the incisions. The surgeon then closes the incisions with minimal scarring. The entire procedure typically lasts less than an hour and is performed under general anesthesia.
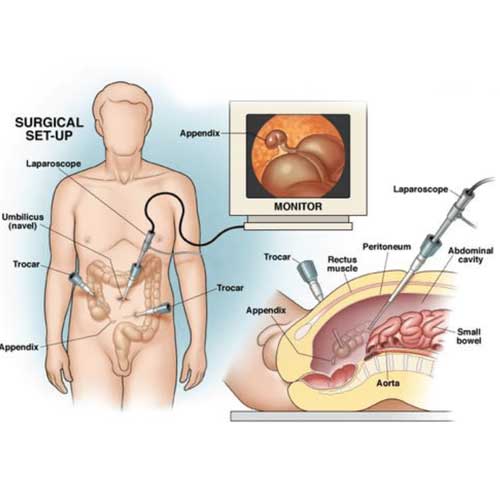
Benefits of Laparoscopic Approach
Laparoscopic surgery offers several advantages over open surgery, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster return to normal activities. It also lowers the risk of wound infections and complications. Patients generally experience less bleeding and can resume eating and walking soon after the operation.
Recovery and Aftercare
Most patients recover quickly from laparoscopic appendectomy, often going home within 24 hours. Full recovery usually takes about one to two weeks. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities for a short period and follow a light diet initially. With proper post-operative care and follow-up, laparoscopic appendectomy is a safe and effective solution for managing acute appendicitis.
Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery
Weight loss surgeries, including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass
Introduction to Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery
Laparoscopic bariatric surgery is a minimally invasive approach to weight loss surgery, designed for individuals struggling with severe obesity. Common procedures include sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass, both of which alter the digestive system to reduce food intake or absorption. These surgeries help achieve significant and sustained weight loss, especially when combined with lifestyle changes and medical support.
Types of Bariatric Procedures
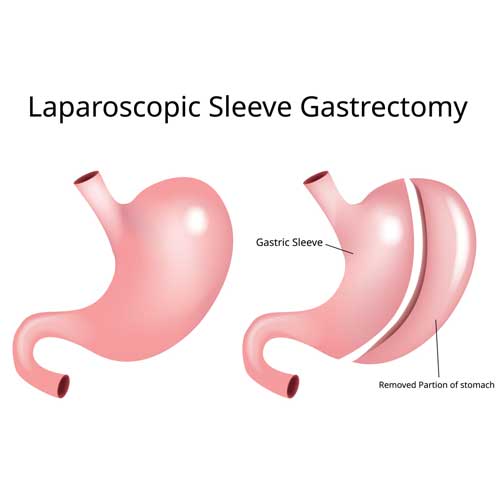
The two most common laparoscopic bariatric surgeries are sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. In sleeve gastrectomy, about 75-80% of the stomach is removed, reducing hunger and food capacity. Gastric bypass involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the intestines, limiting both intake and calorie absorption. Both procedures are effective in improving weight-related health conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Approach
Laparoscopic techniques use small incisions and a camera, resulting in less pain, smaller scars, and quicker recovery compared to open surgery. Patients usually experience shorter hospital stays and return to daily activities sooner. The precision of the laparoscopic method also reduces the risk of complications and infections, making it a preferred choice for many eligible patients.
Post-Surgery Care and Outcomes
Successful weight loss after bariatric surgery depends on a lifelong commitment to healthy eating, exercise, and follow-up care. Most patients lose a significant amount of excess weight within the first year, along with improvements in obesity-related conditions. Nutritional counseling and regular monitoring are essential to ensure long-term health and prevent deficiencies. With proper care, laparoscopic bariatric surgery can be life-changing and life-extending.
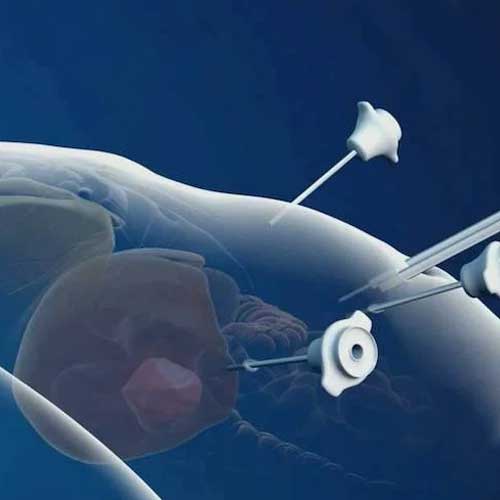
Hernia Repair (Laparoscopic Hernioplasty)
Minimally invasive treatment for inguinal, umbilical, and incisional hernias.
Introduction to Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernioplasty is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat various types of hernias, including inguinal, umbilical, and incisional hernias. A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, often causing pain or a visible bulge. This procedure offers a quicker and less painful alternative to traditional open surgery, promoting faster recovery and reduced recurrence rates.
Procedure and Technique
During laparoscopic hernia repair, surgeons make small incisions in the abdomen and insert a laparoscope (camera) and surgical tools. The herniated tissue is repositioned, and a mesh is placed over the weakened area to reinforce the abdominal wall. The mesh is then secured, and the incisions are closed with minimal scarring. This technique allows for high precision and reduced trauma to surrounding tissues.
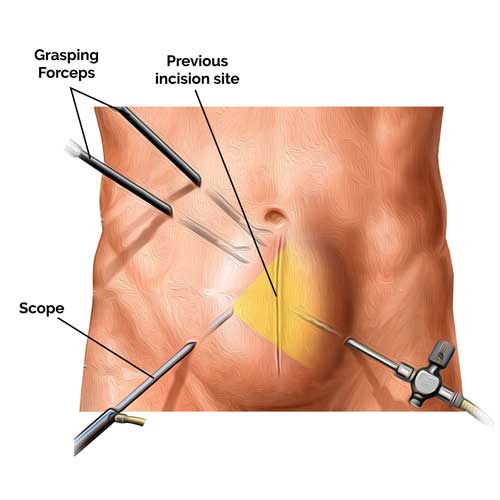
Advantages of Laparoscopic Approach
Laparoscopic hernioplasty provides several benefits over open surgery, including less postoperative pain, smaller incisions, and faster return to normal activities. It is especially beneficial for patients with bilateral or recurrent hernias. The reduced risk of infection and shorter hospital stays make this method a preferred choice for many patients and surgeons alike.
Recovery and Long-Term Outcomes
Most patients recover within one to two weeks after laparoscopic hernia repair. Pain management, light physical activity, and following post-operative instructions are key to a smooth recovery. With proper care, recurrence rates are low, and most individuals resume full activity shortly after surgery. Laparoscopic hernioplasty is a safe, effective, and long-lasting solution for hernia treatment.
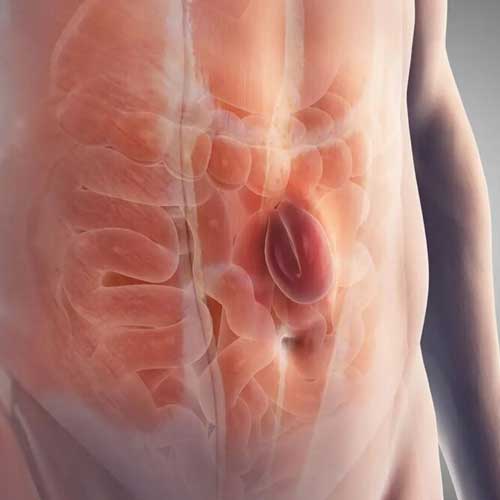
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Advanced uterine surgery with minimal discomfort and quicker recovery
Introduction to Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a modern, minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the uterus. It is commonly performed to treat conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, abnormal bleeding, or uterine cancer. Unlike traditional open surgery, this method uses small incisions and specialized instruments, offering patients less discomfort and a faster return to daily activities.
How the Procedure Works
Surgeons make a few tiny cuts in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope (a thin camera) and surgical tools. The uterus is then carefully detached and removed, often through the vagina or in small pieces. The use of a camera allows for high precision and minimal trauma to surrounding tissues, which contributes to a smoother surgical experience.
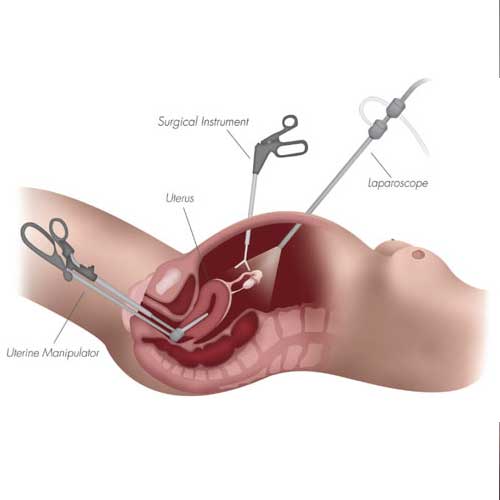
Benefits of Laparoscopic Technique
This approach results in smaller scars, reduced pain, and less blood loss during surgery. Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery compared to traditional hysterectomy. Additionally, there is a lower risk of infection and complications, making it a preferred option for eligible women.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Most women can return home the same day or within 24 hours and resume light activities within a week. Full recovery usually takes 2–4 weeks, depending on the individual's health and the complexity of the procedure. Follow-up care and rest are essential to healing, and most patients report significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life.
Laparoscopic Fundoplication
Surgical treatment for GERD (acid reflux disease)
Introduction to Laparoscopic Fundoplication
Laparoscopic fundoplication is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus. This surgery is recommended for patients who do not respond well to medication or lifestyle changes. It provides long-term relief from symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and chest discomfort.
How the Procedure Works
During the surgery, small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert a camera and surgical tools. The top of the stomach (the fundus) is wrapped around the lower esophagus and stitched into place. This strengthens the valve between the esophagus and stomach, preventing acid from flowing back up. The laparoscopic method ensures greater accuracy and less disruption to surrounding tissues.
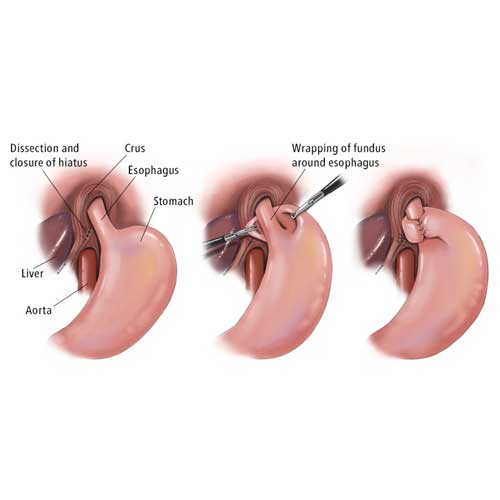
Benefits of the Laparoscopic Approach
Patients benefit from smaller incisions, reduced pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times compared to open surgery. The procedure also helps patients reduce or eliminate the need for long-term acid-suppressing medications. In many cases, it restores normal eating and improves overall quality of life with fewer dietary restrictions.
Recovery and Outlook
Most patients are discharged within one to two days and can return to normal activities within a week or two. A temporary liquid or soft-food diet may be required after surgery to allow proper healing. With proper post-operative care and follow-up, laparoscopic fundoplication offers lasting relief from GERD symptoms and significantly improves daily comfort and digestive health.
Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
Minimally invasive treatment for colorectal cancer and other bowel disorders.
Introduction to Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
Laparoscopic colorectal surgery is a minimally invasive technique used to treat colorectal cancer, diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and other conditions affecting the colon and rectum. This advanced surgical approach uses small incisions and specialized tools to perform complex procedures with greater precision. It offers a safer and faster alternative to traditional open surgery for many patients.
How the Procedure is Performed
Surgeons make a few small cuts in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope (camera) and surgical instruments. The diseased section of the colon or rectum is carefully removed, and the healthy ends are reconnected. In some cases, a temporary or permanent stoma (opening for waste removal) may be required. The laparoscopic method ensures minimal disruption to surrounding tissues and better visualization of the surgical area.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
Compared to open surgery, laparoscopic colorectal procedures lead to less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery. Patients also experience fewer complications, reduced blood loss, and smaller scars. This method is particularly beneficial for elderly patients or those with other medical conditions who may not tolerate open surgery well.
Postoperative Recovery and Outcomes
Most patients can resume normal activities within 1 to 2 weeks, though complete recovery may take a bit longer depending on the procedure’s complexity. A tailored post-operative care plan—including pain management, diet guidance, and physical activity—is essential for full recovery. With proper surgical technique and follow-up, laparoscopic colorectal surgery offers excellent long-term outcomes and significantly improves quality of life.